Stellar/BH Population in AGN Disks: Direct Binary Formation from Capture Objects in Nuclei Clusters
Abstract
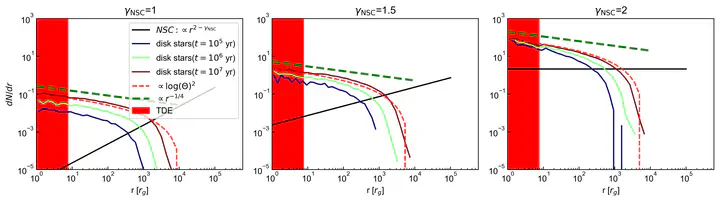
The Active Galatic Nuclei(AGN) disk has been proposed as a potential channel for the merger of binary black holes. The population of massive stars and black holes in AGN disks captured from the nuclei cluster plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency of binary formation and final merger rate within the AGN disks. In this paper, we investigate the capture process using analytical and numerical approaches. We discover a new constant integral of motion for one object capture process. Applying this result to the whole population of the nuclei cluster captured by the AGN disk, we find that the population of captured objects depends on the angular density and eccentricity distribution of the nuclei clusters and is effectively independent of the radial density profile of the nuclei cluster and disk models. An isotropic nuclei cluster with thermal eccentricity distribution predicts a captured profile $dN/dr\propto r^{−1/4}$. The captured objects are found to be dynamically crowded within the disk. Direct binary formation right after the capture would be promising, especially for stars. The conventional migration traps that help pile up single objects in AGN disks for black hole mergers might not be required.